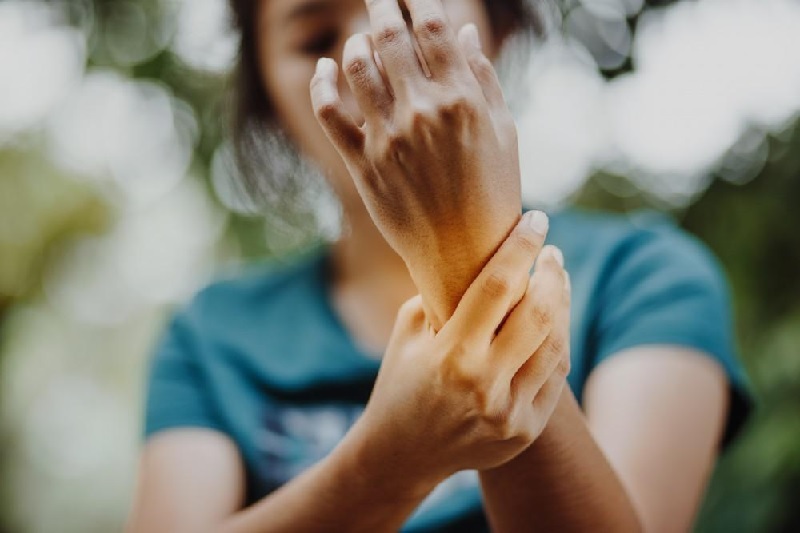
Acute Pain – Acute pain is the most common type of pain that is associated with common injuries like a severe accident or major surgery. Generally, it occurs suddenly and usually goes away as you heal. Acute pain from major surgery may require more intensive therapies or stronger medicines. Minor Acute Pain can be easily treated through over-the-counter medicines like physical therapy or exercise, ibuprofen or acetaminophen, or alternative treatments. Acute pain can turn into chronic pain, if not appropriately treated.
Medical Management of Acute Pain
Acute Pain is discomfort that is less than 3 to 6 months but typically lasts from several weeks to a few moments. It may be categorized as spontaneous or post-traumatic with the trauma planned and is related to skeletal damage. Opioids can be effective in the treatment of acute pain when combined with other analgesics. Some therapies are reserved for more severe pain like opioids. If pain is severe then it is important to recognize that not all acute pain requires opioid therapy. There has been prolonged use of opioids for acute pain.
Types of Acute Pain
Acute pain has two main type spontaneous trauma and elective procedures.
Spontaneous Insult or Trauma: Painful conditions include a sprained ankle, strained ligament, deep laceration, or simple bone fracture. It may be self-treated with rest-ice-compression-elevation therapy and over-the-counter analgesics. A stronger combination of analgesics including opioids is required. All these may require interventions like minor outpatient surgery or splinting but are generally managed with no steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Elective or Planned Procedures: Painful procedures include laparoscopic, arthroscopic, same-day dental or podiatric surgeries. It may be managed with simple analgesics like acetaminophen. A total of 6 to 8 doses of an acetaminophen and opioid combination might be needed if the patient’s discomfort is not controlled with simple analgesics. Painful procedures include surgeries requiring inpatient stays like spine surgery, colorectal surgery, and orthopedic joint replacement.
Treatment Options
Patients are often too focused on the pharmacologic options that are only a small part of the solution. Multimodal treatment is crucial for optimizing pain relief because this approach can also reduce the potential for side effects and different modalities may be additive. Psychosocial interventions, including meditation, deep breathing, and distraction are also central components. The multimodal treatment includes opioids or other analgesics, adjunctive medications, rehabilitation, physical modalities, and nerve blocks.
Opioids: Both patients and providers began looking to opioids to relieve pain and suffering in response to concerns about inadequately treated pain. Sometimes opioids are used for long past resolution of an acutely painful condition.
Simple Analgesics: Simple analgesics like acetaminophen are most effective for treating acute pain because they target the natural inflammation that occurs with an injury. NSAIDs can be more effective than opioids or muscle relaxants for treating acute low back pain (Herbs for Pain).
Topical Analgesics: Menthol and Methyl salicylate are useful in managing musculoskeletal injuries. Many products are available over the counters that are inexpensive. These are all also very effective in reducing swelling and pain caused by muscle strain or sprain.
Also Read
Why Modalert tablet is prescribed?